According to research, more individuals will soon purchase electric vehicles (EVs) wireless charger than conventional gasoline-powered vehicles.
What is the primary distinction between EVs wireless charger and traditional ICE vehicles? EVs emit no emissions, but ICE vehicles emit carbon dioxide as soon as they start.
Because they don’t use gasoline or diesel, EVs are clean. EVs require charging as opposed to refueling. In this blog, we’ll define EV charging and describe how it works.
What is an EV Wireless Charger?
EVs require charging in order to have enough power to function, just like a cell phone. Electric wireless car charger charging is the process of supplying power to the vehicle’s battery using EV charging equipment. The charging station connects to the power grid to charge an EV. Technically, an electric vehicle charging station is known as an EVSE (electric vehicle supply equipment).
EV owners have the choice of charging with a car charger in public, at home or at their place of employment.
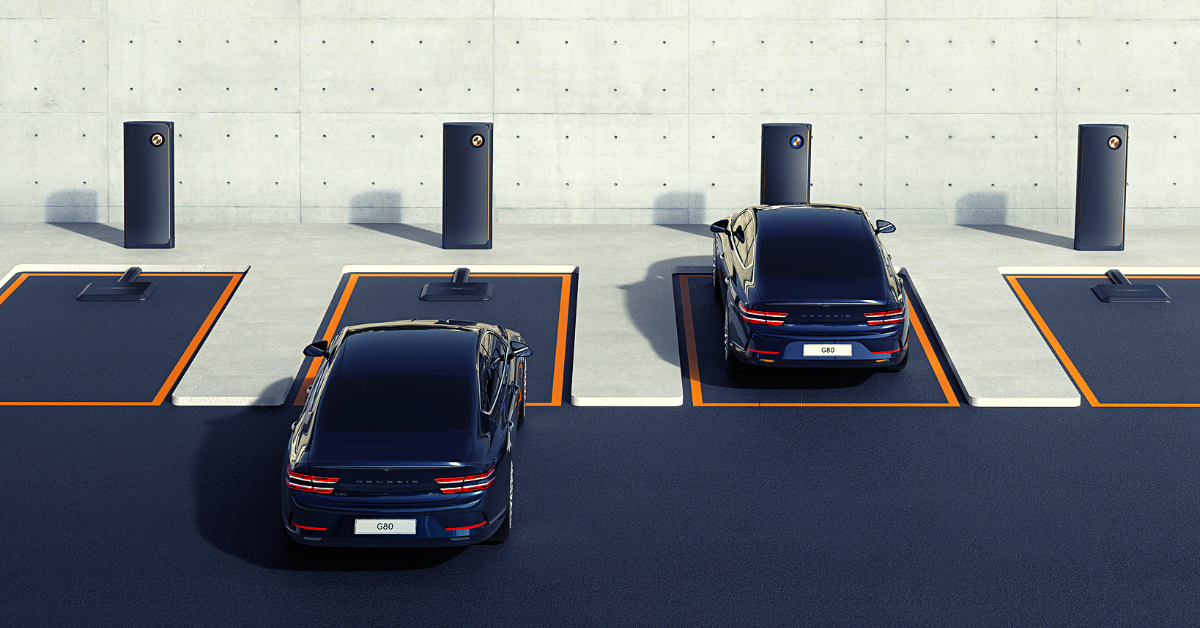
Home charging with a Level 2 charger refers to a residential EV wireless charger.
Commercial electric vehicle wireless charging is available for EV fleets, multi-family homes, and office buildings. Clients and employees use commercial EV charging stations. The business operates numerous electric vehicle charging stations.
How does EV charging work?
An Electric wireless car charger transfers electric current from the grid to the electric vehicle through a socket or connector. An electric vehicle stores electricity in a sizable battery pack to power its electric motor.
The connector of an EV wireless charger is connected to an electric vehicle’s inlet, which is analogous to a conventional vehicle’s gas tank, using a charging cable.
EV batteries only accept direct current (DC) power.
Different Levels Of Electric Vehicle Charging?
There are three levels of electric wireless charger charging: Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3. DC rapid charging, also known as fast charging or DC rapid charging, is the third level of charging.
Any home or garage in the United States has a standard 120-volt wall plug, which used for level 1 charging. Level 1 charging is incredibly sluggish and used for overnight charging at home. An EV battery can take more than 24 hours to fully charge with a car charger in Level 1 charging.
240-volt Level 2 wireless charger is found in households and public charging locations. A Level 2 charger can charge devices up to 15 times faster than a Level 1 charger. A dedicated 208-/240-volt outlet, the same kind of outlet used for an electric clothes dryer, required for Level 2 EV charging stations. The majority of homes lack an additional outlet of this type in the garage or driveway; thus, an electrician can install the dedicated circuit.
The quickest way to charge an electric vehicle is with a DC fast car charger, often known as a rapid charger.
An electric vehicle receives alternating current (AC) from Level 1 and Level 2 chargers, which changed to direct current (DC) by the EV battery. Only DC power applied to an EV battery. Due to the AC/DC conversion process, level 1 and level 2 chargers recharge EVs considerably more slowly.
CHAdeMO (“CHArge de MOve”), the Combined Charging System (CCS), and Tesla Supercharger are the three different methods of Level 3 charging, sometimes known as DC fast charging. Cars using CHAdeMO have a separate port for AC charging, while CCS permits AC/DC charging through the same connector.
Not all EVs are charged using a DC fast car charger. DC fast chargers are used in commercial applications but cannot be installed in homes because they lack electrical capacity. EV drivers don’t need such a quick charge for overnight home charging, and a DC fast charging installation is much more expensive than a Level 2 due to the electrical infrastructure improvements required.
On the other hand, a DC fast charging station can be the best EV charging solution for a business when it comes to commercial applications. For public charging stations and for fleet charging on highways, for instance, DC quick wireless charger is ideal.
Time taken To Charge An EV?
The type of EV charging outlet you are using determines how long it takes to charge an electric vehicle.
Electric vehicles (EVs) charged at a rate of 2 to 5 miles per hour using level 1 chargers.
Level 2 EV charging stations charge up to 15 times more quickly than Level 1 charging stations, with a charging range of 13 to 75 mph.
EV level 2 chargers are easy to use and effective. They are the ideal option for residential charging.
The fastest charging method on the market, level 3 electric vehicle chargers, can charge up to 80% in 10-30 minutes. But not all EVs are compatible with DC fast chargers.
The Cost Of Charging EVs Compared To Gasoline?
According to 2020 research on the cost of charging electric vehicles from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and the Idaho National Laboratory (INL) of the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), electric car owners could save as much as $14,500 on fuel costs over the course of 15 years by driving an EV rather than an ICE vehicle.
The cost of charging an EV varies depending on the location, the efficiency of your EV, how often you use it, the area, and the time of day. According to the report, $0.15/kWh was the national average for charging an electric vehicle.
How much does it cost to operate an internal combustion engine vehicle in comparison?
With gas rates around $3 to $4, the cost per mile varies from $0.13 to $0.22 per gallon (as you know, gas prices fluctuate all the time and this estimate could be at the low end).